Last Modified
1 January 2025
![]()
3D Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship
Structure-Based and Ligand-Based 3D QSARs
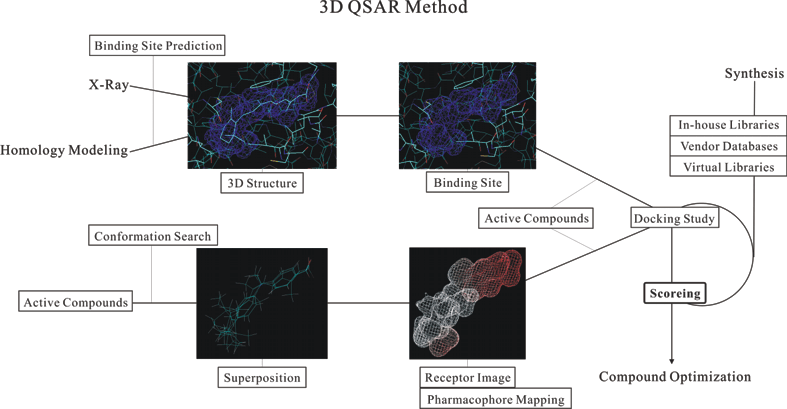
The 3D QSAR method is categorized to the structure-based and ligand-based manners, respectively.
The structure-based 3D QSAR is only available for the case where the 3D structures of a target protein or its homologue bound to the active compound has been experimentally solved using the X-ray crystal structure analysis.
When a homology-modeled target protein is used for this purpose, the numerous combinations of the side chain rotamers in the ligand-binding site must be considered in order to obtain a linear relationship between the in vitro activity of the compounds and the interaction energy (or score) of the complexes.
On the other hand, the ligand-based 3D QSAR is useful, when a fine 3D structure of the target protein are not known experimentally.
Moreover, if a linear relationship is given from the ligand-based 3D QSAR, a receptor image obtained from the superposed structures is mapped by the pharmacophore characteristics of the active compounds, and this receptor image can be further used for the docking study.
May 2005